alternative adapting mechanisms that can overcome AR
blockade, and these also need to be evaluated
[9] .The genomic AR aberrations described in this report
appear common in CRPC but seem to be infrequent in
localized prostate cancers before androgen deprivation.
These probably primarily evolve as a result of treatment-
induced selective pressures, although AR splice variants may
be present in untreated prostate tumors
[10] .Whether these
events appear de novo or are a result of the selection of
subclones that become more prominent after therapy needs
further consideration and may be relevant when selecting
early treatment for both localized and metastatic disease.
The mechanisms resulting in the emergence of these
complex intra-AR rearrangements also merit discussion.
Aberrant DNA damage responses, frequently present in
mCRPC, and the resulting genomic instability may contrib-
ute to the generation of these structural genomic rearran-
gements, particularly when error-prone non-homologous
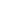
Table 1 – Studies determining androgen receptor aberrations and their impact on clinical outcome
Assay
Aberration
Treatment
Clinical impact
Plasma DNA
Targeted DNA
sequencing
[3]AR CN gain (40%)
AR T878A or L702H mutant (5%)
Abiraterone (80 pts)
AR aberration (CN gain and AR mutant) vs AR CN neutral patients
PSA 50% RR: OR 4.9;
p
= 0.002
aPFS: HR 3.73;
p
= 2 10
6
b,cOS: HR 7.33;
p
= 1.2 10
7
b,cCTCs
RT-PCR
[5]AR-V7 (RNA) positive (19%)
Abiraterone (31 pts)
AR-V7 positive vs AR-V7 negative patients:
PSA 50% RR: 0% vs 68%;
p
= 0.004
aPSA PFS: 1.3 mo vs NR; HR 16.1;
p
<
0.001
b,cClinical/radiological PFS: 2.3 mo vs NR; HR 16.5;
p
<
0.001
b,cOS: 10.6 mo vs NR; HR 12.7;
p
= 0.006
b,cAR-V7 (RNA) positive (39%)
Enzalutamide (31 pts)
AR-V7 positive vs AR-V7 negative patients:
PSA RR: 0% vs 53%;
p
= 0.004
aPSA PFS: 1.4 vs 6.0 mo; HR 7.4;
p
<
0.001
b,cClinical/radiological PFS: 2.1 vs 6.1 mo; HR 8.5;
p
<
0.001
b,cOS: 5.5 mo vs NR; HR 6.9;
p
= 0.002
b,cRT-PCR
[12]AR-V7 (RNA) positive (46%)
Docetaxel (30 pts) and
cabazitaxel (7 pts)
AR-V7 positive vs AR-V7 negative patients:
PSA 50% RR: 41% vs 65%;
p
= 0.19
aPSA PFS: 4.5 vs 6.2 mo; HR 2.1;
p
= 0.06
b,cClinical/radiological PFS: 5.1 vs 6.9 mo; HR 2.8;
p
= 0.02
b,c[11_TD$DIFF]
OS; 9.2 vs 14.7 months; HR 2.5; p=0.11
bc
AR-V7 positive patients demonstrated improved 50% PSA RR
(41% vs 0%;
p
<
0.001
a )PSA PFS (HR 0.22;
p
<
0.001
c),
clinical/radiological PFS (HR 0.26;
p
= 0.001
c ), and OS
(HR 0.83;
p
= 0.76
c) with taxane treatment compared to
AR-targeted therapies (compared to REF; updated analysis).
There was no benefit of taxane treatment over
AR-targeted therapies in AR-V7 negative patients
IF
[6]AR-V7 (protein) positive (12.5%)
Abiraterone, enzalutamide,
and apalutamide (128 pts)
AR-V7 positive vs AR-V7 negative patients:
rPFS: 2.3 vs 14.5 mo; HR 2.3;
p
<
0.001
b,cTime on therapy: 2.1 vs 6.8 mo; HR 4.2;
p
<
0.001
b,cOS: 4.6 mo vs NR; HR 11.45;
p
<
0.001
b,cAR-V7 (protein) positive (28.6%)
Docetaxel, cabazitaxel,
and paclitaxel (63 pts)
AR-V7 positive vs AR-V7 negative patients:
rPFS: 5.3 vs 6.6 mo; HR 1.38;
p
= 0.46
b,cTime on therapy: 3.0 vs 3.7 mo; HR 1.40;
p
= 0.23
b,cOS; 8.9 vs NR; HR 3.74; p=0.001
bc
AR-V7 positive patients had favorable survival on taxane
therapy compared to ARSi (HR 0.24;
p
= 0.035
d[1_TD$DIFF]
)while
[2_TD$DIFF]
AR-V7
negative patients did not
Targeted RNA
sequencing
[1]AR-V (RNA) positive (47%)
Abiraterone (15 pts)
and enzalutamide (2 pts)
AR-V positive vs AR-V negative patients:
PSA 50% RR: 44% vs 12.5%;
p
= 0.29
aPFS HR 4.53;
p
= 0.0105
b,cTissue
IHC
[13]Nuclear AR-V7 (protein) expression Various (37 pts)
Nuclear AR-V7 expression levels by tertiles (3rd vs 2nd vs 1st):
OS from metastatic biopsy: 7.1 vs 10.7 vs 15.6 mo; HR 2.9;
p
= 0.002
b,cCTCs = circulating tumor cells; IF = immunofluorescence; IHC = immunohistochemistry; AR = androgen receptor; CN = copy number; pts = patients;
PSA = prostate-specific antigen; RR = response rate; PFS = progression-free survival; OS = overall survival; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio; RT-
PCR = reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; AR-V7 = androgen receptor variant 7; AR-V = androgen receptor variant; NR = not reached;
ARSi = androgen receptor signaling inhibitor; rPFS = radiological PFS.
a
Fisher’s exact test.
b
Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test.
c
Univariate Cox regression analyses.
d
Multivariate Cox regression analyses.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 2 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 2 0 1 – 2 0 4
202